In order to ascertain an organizations effective CSR policy, practices and culture, the notion of auditing CSR in organizations is becoming key.
The risks of not paying adequate attention to CSR is clear – reputation damage, unhappy employees, not having a competitive advantage, lawsuits, and government scrutiny. Internal audit should focus on these risks and assist management to identify appropriate actions.
A CSR audit should facilitate a better understanding of an organization’s:
- CSR goals and objectives;
- CSR practices, policies and culture; and
- Approach to CSR related issues with respect to its internal decision-making process;
The CSR standards against which auditing professionals can benchmark an organizations performance or behaviour in this area are e.g. Global Reporting Initiative, ISO 26 000 or the Global Compact. Although these standards vary in style and depth, they cover the basics of CSR.
The CSR audit is a tool for decision making and for strategic management
Good example is Qatar Financial Authority were its CSR activities are related with the financial know-how of society. Their CSR activities are increasing awareness with respect to financing and investment ensuring a better calibre professional and a more conscious investor.
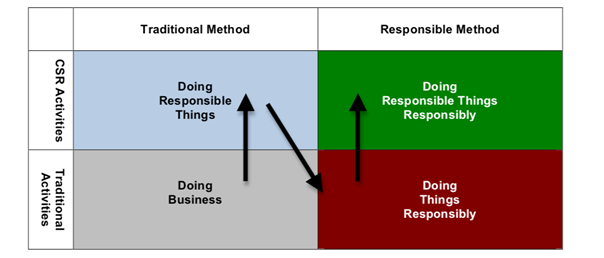
They first had a more integrated approach of CSR by doing what they do but in a more responsible manner i.e. embedding societal considerations in their decision-making process. Eventually it was no longer simply a matter of doing good things to society, or operating one’s organization in a responsible manner, but a further step of integrating CSR with the organization’s objectives, creating a ‘virtuous circle’ for all the stakeholders. This is a highly sustainable model as the success of the business is integrated with the CSR initiatives and there is high commitment from the business at all levels.
How to do a CSR Audit
An internal audit that is intended to cover CSR should start by creating an understanding of the social responsibility issues that affect the organization and its industry. Following that, the audit should review how management reconciles these sometimes-contrary needs.
A CSR audit program can cover all or any of the following risks:
- Effectiveness of the operating framework for CSR implementation
- Effectiveness of implementation of specific, large CSR projects
- Adequacy of internal control and review mechanisms
- Reliability of measures of performance
- Management of risks associated with external factors like regulatory compliance, management of potential adverse NGO attention, etc.
What issues should a CSR Audit cover?
Human Rights:
Fundamental Human Rights, Freedom of association and Collective bargaining, Non-discrimination, Forced labor, Child labor
Business Behavior:
Relations with clients, suppliers and sub-contractors, Prevention of corruption and anti-competitive practices
Human Resources:
Labor relations, Working conditions, health and safety, career development and training, Remuneration system
Corporate Governance:
Board of Directors, Audit and internal controls, Treatment of shareholders,
Executive remuneration
Environment:
Incorporation of environmental considerations into the manufacturing and distribution of products, and into their use and disposal
Community Involvement:
Impacts on local communities, contribution to social and economic development, General interest causes
Contact us for more information on CSR Audits at info@flagship.cz.

